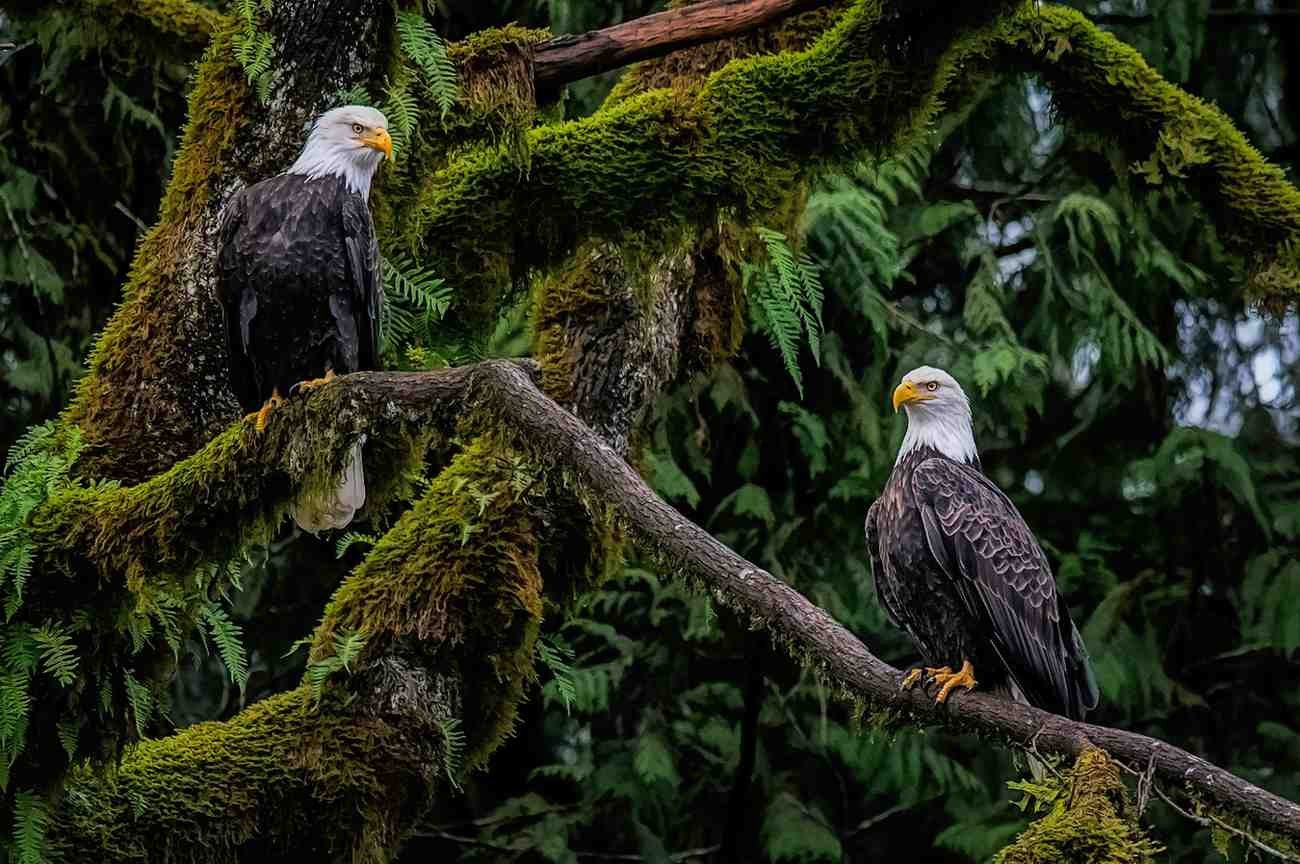
Birds are one in every one of nature’s most fascinating creations, embodying grace, beauty, and thriller. Among them, the Hancock Bird sticks out as a particularly intriguing species. Though less widely known than iconic birds like eagles or peacocks, the Hancock Bird has garnered attention for its particular physical tendencies, adaptive behaviors, and ecological significance. In this text, we explore the arena of the Han cock Bird, unraveling its mysteries in tremendous detail.
Origins and History of the Hancock Bird
The Hancock Bird, named after the famous ornithologist Dr. William Hancock, turned into first diagnosed within the mid-twentieth century. Dr. Hancock found the fowl at the same time as reading avian species in faraway tropical regions. Although to start with the idea to belong to an existing genus, in addition studies found out its particular characteristics, warranting class as a wonderful species.
Over the many years, the Hancock Bird has grown to be a symbol of conservation efforts and a topic of fascination for birdwatchers globally. Its elusive nature makes it a prized sighting for lovers, further elevating its fame inside the ornithological community.
Physical Characteristics
One of the maximum placing features of the Hancock Bird is its vibrant plumage, which varies among males and females. Male Hancock Birds regularly boast iridescent feathers with shades of emerald green, sapphire blue, and fiery orange. These colors are specifically vibrant throughout the mating season, designed to attract potential pals. Females, then again, showcase greater muted tones of brown and grey, supplying natural camouflage at the same time as nesting.
The Hancock Bird has a slim frame, commonly measuring 10–12 inches in duration. Its wingspan, ranging from 12 to fifteen inches, lets in for agile flight through dense foliage. Its beak is curved, perfectly suited for eating seeds, culmination, and small insects. The bird’s sharp claws permit it to perch securely on branches, even in windy situations.
Habitat and Distribution
The Hancock Bird predominantly inhabits tropical and subtropical areas, thriving in regions with considerable plant life and water resources. Native to parts of Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, it’s far most commonly located in dense rainforests, mangroves, and riverbanks.
- Southeast Asia: In countries like Thailand and Malaysia, the Hancock Bird prefers evergreen forests, in which its colourful hues blend harmoniously with lush greenery.
- Africa: In nations including Ghana and Uganda, it could be noticed in savannas and wooded areas close to water bodies.
- South America: The Amazon rainforest serves as a good sized habitat for the Hancock Bird, with sightings pronounced near Brazil’s important river structures.
Though ordinarily woodland-dwelling, some populations have tailored to urban fringes due to habitat loss. They are now and again visible in parks and gardens with dense tree cowl, demonstrating their adaptability.
Behavior and Social Structure
The Hancock Bird is understood for its social and cooperative nature. While a few birds are solitary, Hancock Birds shape small flocks which include 10–20 individuals. These groups play a crucial role in making sure protection, as members alert each other to predators.
Feeding Habits
The Hancock Bird’s weight-reduction plan is numerous, reflecting its omnivorous nature. Insects like beetles and caterpillars shape a significant part of its diet, particularly for the duration of the breeding season whilst protein is important for chicks. Outside of this era, it consumes diverse culmination, seeds, and berries, contributing to seed dispersal and forest regeneration.
Mating and Nesting
The mating rituals of the Hancock Bird are a spectacle. Males carry out complicated dances, spreading their wings and fluffing their feathers to show off their vibrant shades. They also sing intricate songs, with each male having a completely unique melody to woo ability associates.
Once a couple bonds, they build nests together using twigs, leaves, and grass. These nests are often hidden inside dense foliage to guard eggs from predators. Typically, the woman lays 2–4 eggs, which each parent incubates and shields.
Ecological Importance
The Hancock Bird plays a pivotal function in maintaining atmosphere balance. Its sports contribute to:
- Seed Dispersal: By consuming fruits and excreting seeds in special locations, the Hancock Bird facilitates wooded area regeneration.
- Insect Control: By feeding on bugs, it enables control of pest populations, reaping rewards agriculture in close by areas.
- Biodiversity Maintenance: As part of the food chain, the Han cock Bird helps larger predators, ensuring ecological equilibrium.
Additionally, its presence serves as a hallmark of environmental health. A thriving Hancock Bird populace often signifies a well-balanced and biodiverse habitat.
Threats and Conservation Challenges
Despite its ecological importance, the Hancock Bird faces severa threats. The maximum urgent demanding situations encompass:
- Habitat Destruction: Logging, deforestation, and urban growth have extensively reduced its herbal habitats.
- Climate Change: Shifts in temperature and rainfall styles disrupt breeding and food availability.
- Illegal Trade: The Hancock Bird’s colourful plumage makes it a goal for unlawful wildlife trafficking, with some people offered as exotic pets.
To combat those threats, conservation businesses have initiated efforts which include:
- Establishing Protected Areas: Wildlife reserves and national parks offer secure havens for the Hancock Bird.
- Community Engagement: Educating nearby communities about the chook’s ecological importance encourages sustainable practices.
- Legislation: Governments in regions where the Han cock Bird is living have carried out stricter laws to slash hunting and illegal trade.
How You Can Help
If you’re passionate about wildlife, there are numerous approaches to make a contribution to the conservation of the Hancock Bird:
- Support Conservation Programs: Donate to agencies running to maintain their habitats.
- Raise Awareness: Share records approximately the Han cock Bird and its ecological role along with your network.
- Practice Sustainable Living: Reduce your carbon footprint to mitigate climate alternatives’ consequences on wildlife.
- Avoid Illegal Products: Refrain from shopping for individual pets or items made from endangered species.
Conclusion
The Hancock Bird is a testomony to the difficult beauty and interdependence of existence on Earth. Its bright colorations, melodious songs, and ecological contributions make it a high-quality species deserving of admiration and safety. However, the challenges it faces highlight the urgency of conservation efforts to ensure its survival.
By gaining knowledge of approximately and assisting the Hancock Bird, we not handiest assist preserve an unmarried species but additionally contribute to the fitness and power of ecosystems worldwide. Whether you’re a birdwatcher, a conservationist, or genuinely a nature enthusiast, the Hancock Bird serves as a reminder of the wonders of biodiversity and our shared obligation to shield it.
FAQs About the Hancock Bird
Q1: Is the Hancock Bird endangered?
Some subspecies are categorized as prone because of habitat loss and declining populations, although others remain quite solid.
Q2: What does the Hancock Bird characterize in local cultures?
In a few areas, the Hancock Bird is considered a symbol of renewal and concord because of its function in forest regeneration.
Q3: Can I appeal to Hancock Birds to my lawn?
If you stay in their local regions, planting fruit-bearing trees and ensuring a water supply can inspire their presence.
Q4: Are Hancock Birds migratory?
Some populations show off seasonal migration, moving to warmer regions throughout chillier months, at the same time as others continue to be in their habitats yr-spherical.
Q5: What is the lifespan of a Hancock Bird?
In the wild, Hancock Birds typically stay 6–eight years, even though a few had been known to live over a decade in protected environments.